



1. Definition
Total Knee Replacement (TKR), also known as total knee arthroplasty (TKA), is a surgical procedure performed to:
2. Purpose
3. When is TKR Recommended?

Replaces both sides of the knee joint.
Involves removal of damaged cartilage and bone.
Implant consists of metal and plastic components.
Restores full range of motion.

Also known as unicompartmental knee replacement.
Only one side of the knee is replaced.
Suitable for localized knee arthritis.
Less invasive with faster recovery.

Advanced surgical technique using robotic technology.
Precise implant positioning.
Minimally invasive, offering greater accuracy.

For distal femur fractures (near the knee).
Nail inserted through the knee joint.
Stabilizes the femur and allows early mobility.

Performed if the initial TKR fails.
Replaces the original implant with a new one.
Treats implant loosening, wear, or infection.
Persistent pain in the knee.
Worsens with movement or weight-bearing.
Difficulty bending or straightening the knee.
Swelling and inflammation around the joint.
Reduced range of motion.
Difficulty walking or climbing stairs.
Feeling of the knee giving out.
Reduced balance and stability.
Bowing or knock-knee deformity.
Visible misalignment of the leg.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Reduces stress on knee joints.
Low-impact activities (swimming, walking).
Strengthens knee muscles and improves stability.
Avoid repetitive stress on the knees.
Use proper footwear.
Omega-3-rich foods (salmon, flaxseeds).
Reduces joint inflammation.
Physical therapy for minor knee issues.
Prevents long-term damage.
NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections.
Reduces inflammation and pain.
Strengthening exercises before and after surgery.
Improves flexibility and range of motion.
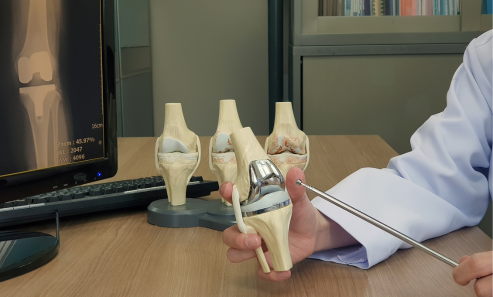
TKR procedure for severe joint damage.
Restores knee function and relieves pain.

Imaging tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans.
Pre-surgery assessment: Blood tests and medical evaluation.
Anesthesia consultation: General or spinal anesthesia

Incision made over the knee joint.
Damaged cartilage and bone are removed.
Artificial implant components inserted.
Metal femoral component and plastic spacer replace damaged surfaces.
Incision closed with sutures or staples.
Dressing and bandage applied.

2-4 days of hospitalization
Pain management with analgesics.
Use of walker or crutches initially.
Gradual transition to full weight-bearing.
Antibiotics to prevent infection.
Blood thinners to prevent clots.
Regular X-rays to monitor implant positioning.
Physical therapy for mobility restoration.

Traditional open surgery.
Removes damaged knee components.
Replaces with metal and plastic implants.
Smaller incision with less tissue damage.
Faster recovery and reduced pain.
Uses robotic technology for precision.
More accurate implant positioning.
Only the damaged compartment replaced.
Preserves healthy bone.