



Definition
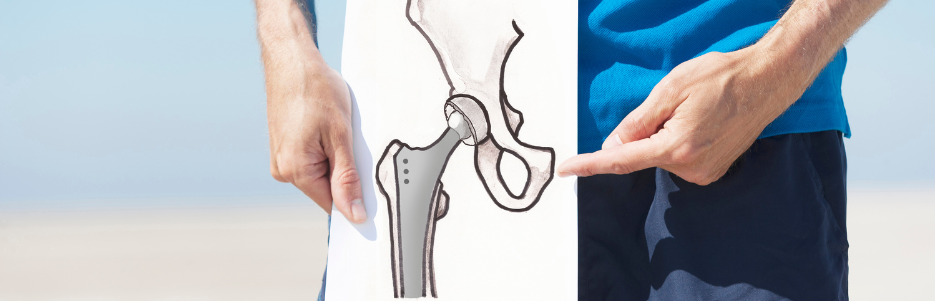
Total Hip Replacement (THR), also known as Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA), is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial implant.
Purpose of THR

Cemented THR: Uses a special bone cement to fix the implant. Suitable for older, less active patients.
Uncemented THR: The implant is press-fitted, allowing bone to grow into it. Common for younger, active patients.

Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty): Replaces only the femoral head. Common for hip fractures.
Total Hip Replacement (THR): Replaces both the femoral head and acetabulum (hip socket).

Traditional THR: Requires a larger incision with more muscle cutting.
Minimally Invasive THR: Smaller incisions with less muscle damage, leading to faster recovery.

Uses robotic technology for precise implant positioning.
Provides better alignment and longer-lasting results.
Persistent pain in the hip or groin.
Worsens with activity, even at rest.
Trouble with standing, walking, or climbing stairs.
Limping due to hip joint damage.
Difficulty moving the hip, especially bending or rotating.
Painful stiffness in the morning or after sitting for long periods.
Bowing or misalignment of the hip joint.
Shortening of the affected leg.
Reduces stress on the hip joints.
Low-impact exercises (swimming, cycling) keep joints flexible.
Omega-3-rich foods reduce inflammation.
Calcium and Vitamin D support bone strength.
Physical therapy or medications for minor hip problems.
Prevents long-term joint damage.
Reduce jumping and heavy lifting to protect joints.
NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections to manage pain.
Strengthening exercises before and after surgery.
THR surgery when pain becomes unmanageable

X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to assess hip damage.
Medical evaluation (blood tests, anesthesia consultation).

Incision is made over the hip joint.
Damaged cartilage and bone are removed.
Damaged bone and cartilage are removed.
Metal, plastic, or ceramic implant is inserted.
Hip joint is repositioned, and incision is closed.

Takes 1-2 hours depending on complexity.

2-4 days depending on healing progress.
Pain management with analgesics.
Use of walker or crutches initially.
Full mobility returns over 6-12 weeks.
Painkillers and blood thinners to prevent clots.
Exercises to strengthen hip muscles and improve movement.

Open surgery with a large incision.
Uses smaller incisions and less tissue damage.
Robotic precision for better implant placement.
Preserves more bone (used in younger patients).