




Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF) is a surgical procedure used to:
Femur, tibia, humerus, radius, ulna, or fibula fractures.
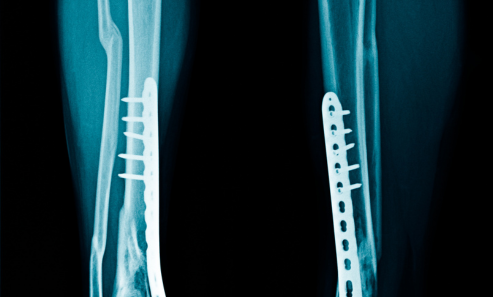
Plates, screws, or rods inserted along the bone.
Restores proper alignment and function.
Ankle, wrist, elbow, shoulder, or knee fractures.
Fixation devices stabilize the joint.
Prevents arthritis or stiffness.
Hip fractures in elderly patients.
Screws, plates, or rods inserted.
Prevents hip displacement and promotes mobility.
Complex pelvic fractures require internal fixation.
Reduces pain and prevents complications.
Plates and screws stabilize the pelvis.
Used for metacarpal or phalangeal fractures.
Helps restore fine motor functions.
Plates and screws secure small bones.
Doctors may recommend angiography if a patient experiences:
Severe Pain and Swelling

Bone Deformity

Loss of Mobility or Function

Open Fractures

Non-Healing Fractures
Calcium and Vitamin D-rich diet.
Strengthens bones and prevents fractures.
Weight-bearing exercises enhance bone density.
Improves balance and reduces fall risk.
Use handrails, non-slip mats, and proper lighting.
Especially important for the elderly.
Bone density screening for at-risk individuals.
Use of osteoporosis medications.
Wear helmets and padding during high-risk activities.
Reduces fracture risks.
Surgical realignment of fractured bones.
Reduces deformity and restores function.
Plates, screws, rods, or wires inserted.
Provides stability during healing.
Used for severe fractures or bone loss.
Bone graft enhances healing.

Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI.
Anesthesia consultation: General or regional anesthesia.
Fasting before surgery.

Incision made over the fracture site.
Bone exposed for realignment.
Fractured bones are realigned.
Internal fixation with screws, plates, rods, or wires.
Incision closed with stitches or staples.
Bandages and dressings applied.

1-3 days of hospitalization.
Pain management with analgesics.
Use of crutches or walkers for lower limb fractures.
Limited weight-bearing for several weeks.
Antibiotics to prevent infection.
Blood thinners to prevent clots.
Regular X-rays to monitor bone healing.
Physical therapy for mobility restoration.

Plates and screws hold bones in place.
Common for long bone fractures.
Rod inserted inside the bone canal.
Stabilizes femur, tibia, or humerus fractures.
Used for small bone fractures.
Common in hand or foot fractures.