



Comprehensive Guide to Implant Removal and Closed Reduction
1.Definition
2. Purpose
3. When is the Procedure Recommended?

For small or superficial implants.
Includes removal of screws, plates, or pins.
Performed under local or general anesthesia.

For deeply embedded or large implants.
Involves extensive dissection.
May require open surgery.

Used for fractures or dislocations that do not require surgery.
Performed by manually realigning the bone.
X-ray guidance used to confirm bone alignment.

Implant removal combined with closed reduction.
Used when bone misalignment occurs after implant removal.
Improves bone positioning and stability.
Chronic pain or irritation around the implant.
Worsens with movement or weight-bearing.
Restricted range of motion.
Stiffness around the implant area.
Swelling, redness, and warmth at the implant site.
Drainage or pus formation.
Visible bone displacement or deformity.
Irregular bone contour.
Instability or clicking near the implant site.
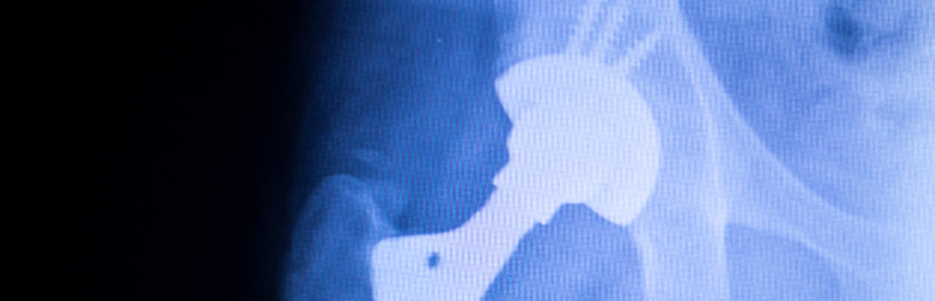
X-ray shows movement or detachment of the implant.

Follow post-surgical protocols.
Avoid putting excess weight or strain on the implant area.
Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake.
Prevent osteoporosis.
Periodic X-rays to monitor implant stability.
Detect early signs of loosening or misalignment.
Use knee or joint braces during high-impact activities.
Prevent accidental falls or collisions.
Proper wound care after surgery.
Take antibiotics as prescribed.
NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) to reduce inflammation.
Corticosteroid injections for severe pain.
Strengthens the surrounding muscles.
Restores range of motion and flexibility.
Knee or joint braces for stability.
Reduces strain during physical activity.
Indicated for chronic pain or implant failure.
Performed to reduce discomfort and improve mobility.

Imaging tests: X-rays or CT scans to locate the implant.
Pre-surgical assessment: Blood tests and evaluation.
Anesthesia consultation: Local or general anesthesia.

Closed reduction performed first (if needed).
External manipulation to align the bone.
Incision made over the implant.
Implant hardware removed.
Bone inspected for signs of infection or damage.
Cleaning and debridement performed.
Incisions closed with stitches or staples.
Dressing and bandage applied.

Outpatient procedure (same-day discharge).
Pain management with medications.
Use of crutches or walker for 1-2 weeks.
Gradual return to physical activity.
Painkillers and antibiotics to prevent infection.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for swelling.
Physical therapy to regain strength.
Regular check-ups and imaging.

Performed for superficial implants.
Minimally invasive.
For deep implants or complex fractures.
Requires open surgery.
Non-surgical method.
Realigns fractures and stabilizes with a cast or brace.